
Blockchain technology has been an obsession on Wall Street for years, as banks try to apply the notion of a shared, permanent ledger to antiquated financial plumbing. It could speed up transactions and make record keeping flawless. But the benefits of the technology could soon flow to an unlikely group: songwriters seeking the millions of dollars in royalties that the world’s biggest streaming platforms owe them.
At the end of April, Spotify acquired a little known New York startup called Mediachain Labs. The Brooklyn outfit was working on ways to track images over the internet, while creating an indelible link back to their creators. This was to be done on a blockchain—a decentralized, permanent ledger—that could reconcile millions of transactions while guaranteeing perfect transparency. The idea could well be applied to music.
The acquisition raises the prospect that Spotify could use the technology to solve one of the music business’ most vexing problems, while finally bringing blockchain tech to the mainstream. The move could even prevent Spotify’s long awaited public stock offering from being torpedoed by lawsuits.
Royal mess
You see, the music business has a massive database problem. Last March, Spotify paid up to $30 million in owed royalties to music publishers and songwriters. YouTube followed suit in December, settling for a reported $40 million (paywall) over unpaid royalties. Spotify explained (paywall) that it couldn’t pay the money out because it didn’t know who to pay, or how much.
Spotify’s defense has some truth to it. Splitting the money from music is a supremely complicated business. The revenue from each streamed song has to be divided among intermediaries like record labels, performing rights organizations, and publishers. Then it’s sub-divided until it trickles down to songwriters and performers. To compound the complexity, there’s no foolproof way of identifying those parties for a given song.
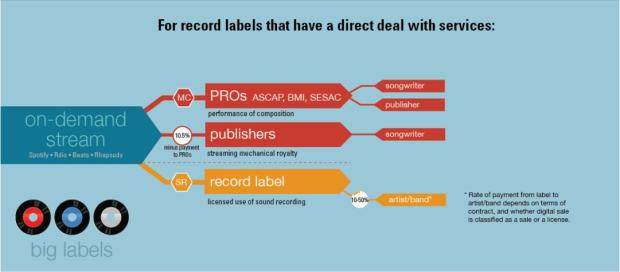
This is the problem of attribution, which has intensified as streaming platforms account for ever larger chunks of music industry revenues. It’s an “existential threat” for firms like Spotify, says George Howard, a professor of management at the Berklee College of Music. Spotify, or any streaming platform, could be sued over and over again because it simply can’t reconcile all its streams with their authors.
To be sure, not every stream is untraceable. In many cases, streams are correctly matched to publishers and writers. Spotify has paid out $5 billion in royalties since it was founded in 2006; far more than the $30 million in owed royalties it settled for over the same period. Still, it’s clear that significant chunk of money isn’t finding its way to its rightful recipients—publishers and songwriters, in particular.
A cryptographic solution
The music business knows it has a problem, and it’s tried to solve it before. But each time, efforts to construct databases fell to coordination problems, or industry politics. Someone had to control the database, after all, bringing self-interest to the fore. As longtime Universal Music executive Larry Kenswil told the authors of a 2015 Berklee research report (pdf): “When the technology industry comes calling to ask what music needs to solve its data issues, the music industry doesn’t often know. They are too busy fighting amongst themselves about their share of the pie.”

This is the problem of attribution, which has intensified as streaming platforms account for ever larger chunks of music industry revenues. It’s an “existential threat” for firms like Spotify, says George Howard, a professor of management at the Berklee College of Music. Spotify, or any streaming platform, could be sued over and over again because it simply can’t reconcile all its streams with their authors.
To be sure, not every stream is untraceable. In many cases, streams are correctly matched to publishers and writers. Spotify has paid out $5 billion in royalties since it was founded in 2006; far more than the $30 million in owed royalties it settled for over the same period. Still, it’s clear that significant chunk of money isn’t finding its way to its rightful recipients—publishers and songwriters, in particular.
A cryptographic solution
The music business knows it has a problem, and it’s tried to solve it before. But each time, efforts to construct databases fell to coordination problems, or industry politics. Someone had to control the database, after all, bringing self-interest to the fore. As longtime Universal Music executive Larry Kenswil told the authors of a 2015 Berklee research report (pdf): “When the technology industry comes calling to ask what music needs to solve its data issues, the music industry doesn’t often know. They are too busy fighting amongst themselves about their share of the pie.”
This is the problem of attribution, which has intensified as streaming platforms account for ever larger chunks of music industry revenues. It’s an “existential threat” for firms like Spotify, says George Howard, a professor of management at the Berklee College of Music. Spotify, or any streaming platform, could be sued over and over again because it simply can’t reconcile all its streams with their authors.
To be sure, not every stream is untraceable. In many cases, streams are correctly matched to publishers and writers. Spotify has paid out $5 billion in royalties since it was founded in 2006; far more than the $30 million in owed royalties it settled for over the same period. Still, it’s clear that significant chunk of money isn’t finding its way to its rightful recipients—publishers and songwriters, in particular.
A cryptographic solution
The music business knows it has a problem, and it’s tried to solve it before. But each time, efforts to construct databases fell to coordination problems, or industry politics. Someone had to control the database, after all, bringing self-interest to the fore. As longtime Universal Music executive Larry Kenswil told the authors of a 2015 Berklee research report (pdf): “When the technology industry comes calling to ask what music needs to solve its data issues, the music industry doesn’t often know. They are too busy fighting amongst themselves about their share of the pie.”
A Spotify blockchain would mean the tech has finally “grown up,” says Simon Taylor, co-founder of fintech consultancy 11:FS. “Blockchain was always likely to be taken mass market by someone other than banks,” he says. Indeed, another tech company, Alphabet’s DeepMind artificial intelligence unit, has also launched its own blockchain effort in March to handle British health records.
Of course, the Mediachain Labs deal could just be a straightforward ”acqui-hire” to bring smart database thinkers on board. Something similar happened when Airbnb acquired a bitcoin micro-payments startup called Changetip last April. The lodging startup had expressed an interest in blockchain technology before the acquisition, but nothing blockchain-related has come out of the deal so far.
There are other barriers to blockchain adoption in the music industry, even if Spotify moves forward with it. Howard, the Berklee professor, points out that rights holders could start building their own private blockchains, mirroring financial institutions, which are obsessed with keeping data proprietary. This would simply create a new series of silos, defeating the purpose of a universal database. Howard also says the biggest stars in music need to get on board with the tech, or else it’ll never gain the network effects required for an industry to embrace it.
That means musicians like Drake, Justin Bieber, and Rihanna, who were Spotify’s most streamed artists last year, need to get comfortable with the idea that their royalties are going to be tracked on a blockchain—and maybe even paid out on one—before the fantasy of music on the blockchain takes shape.








